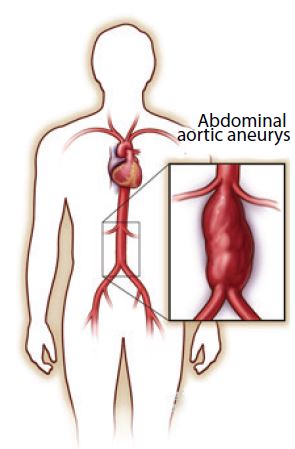
WHAT IS AN ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM (AAA)?
The aorta is the largest artery in your body, and it carries oxygen-rich blood pumped out of, or away from, your heart. Your aorta runs through your chest, where it is called the thoracic aorta. When it reaches your abdomen, it is called the abdominal aorta. The abdominal aorta supplies blood to the lower part of the body. In the abdomen, just below the navel, the aorta splits into two branches, called the iliac arteries, which carry blood into each leg.
When a weak area of the abdominal aorta expands or bulges, it is called an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA). The pressure from blood flowing through your abdominal aorta can cause a weakened part of the aorta to bulge, much like a balloon. A normal aorta is about 1 inch (or about 2 centimeters) in diameter. However, an AAA can stretch the aorta beyond its safety margin as it expands. Aneurysms are a health risk because they can burst or rupture. A ruptured aneurysm can cause severe internal bleeding, which can lead to shock or even death.
Less commonly, AAA can cause another serious health problem called embolization. Clots or debris can form inside the aneurysm and travel to blood vessels leading to other organs in your body. If one of these blood vessels becomes blocked, it can cause severe pain or even more serious problems, such as limb loss.
Each year, physicians diagnose approximately 200,000 people in the United States with AAA. Of those 200,000, nearly 15,000 may have AAA threatening enough to cause death from its rupture if not treated.
Fortunately, especially when diagnosed early before it causes symptoms, an AAA can be treated, or even cured, with highly effective and safe treatments.
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS?
Although you may initially not feel any symptoms with AAA, if you develop symptoms, you may experience one or more of the following:
- A pulsing feeling in your abdomen, similar to a heartbeat
- Severe, sudden pain in your abdomen or lower back. If this is the case, your aneurysm may be about to burst
- On rare occasions, your feet may develop pain, discoloration, or sores on the toes or feet because of material shed from the aneurysm
If your aneurysm bursts, you may suddenly feel intense weakness, dizziness, or pain, and you may eventually lose consciousness. This is a life-threatening situation and you should seek medical attention immediately.
WHAT CAUSES AN ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM?
Physicians and researchers are not quite sure what actually causes an AAA to form in some people. The leading thought is that the aneurysm may be caused by inflammation in the aorta, which may cause its wall to weaken or break down. Some researchers believe that this inflammation can be associated with atherosclerosis (also called hardening of the arteries) or risk factors that contribute to atherosclerosis, such as high blood pressure (hypertension) and smoking. In atherosclerosis fatty deposits, called plaque, build up in an artery. Over time, this buildup causes the artery to narrow, stiffen and possibly weaken. Besides atherosclerosis, other factors that can increase your risk of AAA include:
- Being a man older than 60 years
- Having an immediate relative, such as a mother or brother, who has had AAA
- Having high blood pressure
- Smoking
Your risk of developing AAA increases as you age. AAA is more common in men than in women.
WHAT TESTS WILL I NEED?
Abdominal aortic aneurysms that are not causing symptoms are most often found when a physician is performing an imaging test, such as an ultrasound or CT scan, for another condition. Sometimes your physician may feel a large pulsing mass in your abdomen on a routine physical examination. If your physician suspects that you may have AAA, he or she may recommend one of the following tests to confirm the suspicion:
- Abdominal ultrasound
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
HOW IS AN ABDOMINAL AORTIC ANEURYSM TREATED?
Watchful waiting If your AAA is small, your physician may recommend “watchful waiting,” which means that you will be monitored every 6-12 months for signs of changes in the aneurysm size. Your physician may schedule you for regular CT scans or ultrasounds to watch the aneurysm. This method is usually used for aneurysms that are smaller than about 2 inches (roughly 5.0 to 5.5 centimeters) in diameter. If you also have high blood pressure, your physician may prescribe blood pressure medication to lower the pressure on the weakened area of the aneurysm. If you smoke, you should obtain help to stop smoking. An aneurysm will not “go away” by itself. It is extremely important to continue to follow up with your physician as directed because the aneurysm may enlarge to a dangerous size over time. It could eventually burst if this is not detected and treated.
Open Surgical aneurysm repair A vascular surgeon may recommend that you have a surgical procedure called open aneurysm repair if your aneurysm is causing symptoms, or is larger than about 2 inches (roughly 5.0 to 5.5 centimeters), or is enlarging under observation.
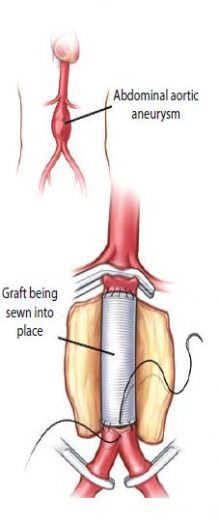
During an open aneurysm repair, also known as surgical aneurysm repair, your surgeon makes an incision in your abdomen and replaces the weakened part of your aorta with a tube-like replacement called an aortic graft. This graft is made of a strong, durable, man-made plastic material, such as Dacron®, in the size and shape of the healthy aorta. The strong tube takes the place of the weakened section in your aorta and allows your blood to pass easily through it. Following the surgery, you may stay in the hospital for 4 to 7 days. Depending upon your circumstances, you may also require 6 weeks to 3 months for a complete recovery. More than 90 percent of open aneurysm repairs are successful for the long term
Endovascular stent graft Instead of open aneurysm repair, your vascular surgeon may consider a newer procedure called an endovascular stent graft. Endovascular means that the treatment is performed inside your artery using long, thin tubes called catheters that are threaded through your blood vessels. This procedure is less invasive, meaning that your surgeon will usually need to make only small incisions in your groin area through which to thread the catheters. During the procedure, your surgeon will use live x-ray pictures viewed on a video screen to guide a fabric and metal tube, called an endovascular stent graft (or endograft), to the site of the aneurysm. Like the graft in open surgery, the endovascular stent graft also strengthens the aorta. Your recovery time for endovascular stent grafting is usually shorter than for the open surgery, and your hospital stay may be reduced to 2 to 3 days. However, this procedure requires more frequent follow-up visits with imaging procedures, usually CT scans, after endograft placement to be sure the graft continues to function properly. Also, the endograft is more likely to require periodic maintenance procedures than does the open procedure. In addition, your aneurysm may not have the shape that is suitable for this procedure, since not all patients are candidates for endovascular repair because of the extent of the aneurysm, or its relationship to the renal (kidney) arteries, or other issues. While the endovascular stent graft may be a good option for some patients who have suitable aneurysms and who have medical conditions increasing their risk, in some other cases, open aneurysm repair may still be the best way to cure AAA. Your vascular surgeon will help you decide what is the best method of treatment for your particular situation.

 Vi
Vi