With the desire to bring modern diagnostic and treatment methods to the community, FV Hospital deploys the application of endobronchial ultrasound technique to help diagnose lymph nodes in the chest and accurately assess the stage of lung cancer, thereby providing appropriate and effective treatment. FV is one of the few hospitals in Vietnam to apply and implement this technique at the Internal Medicine Department, Pulmonology Unit by Nguyen Van Tho PhD, MD.
Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) is a bronchoscopy technique combined with ultrasound to observe and evaluate parabronchial lesions such as paratracheal tumours, hilar nodes, and central lymph nodes, and ventricular or peripheral lung lesions where conventional endoscopy is difficult to reach. Ultrasound bronchoscopy has two types of probes: Radial probe EBUS-(RP-EBUS) for peripheral lung lesions and convex probe EBUS (CP-EBUS) for hilar, mediastinal, or paratracheal tumours.
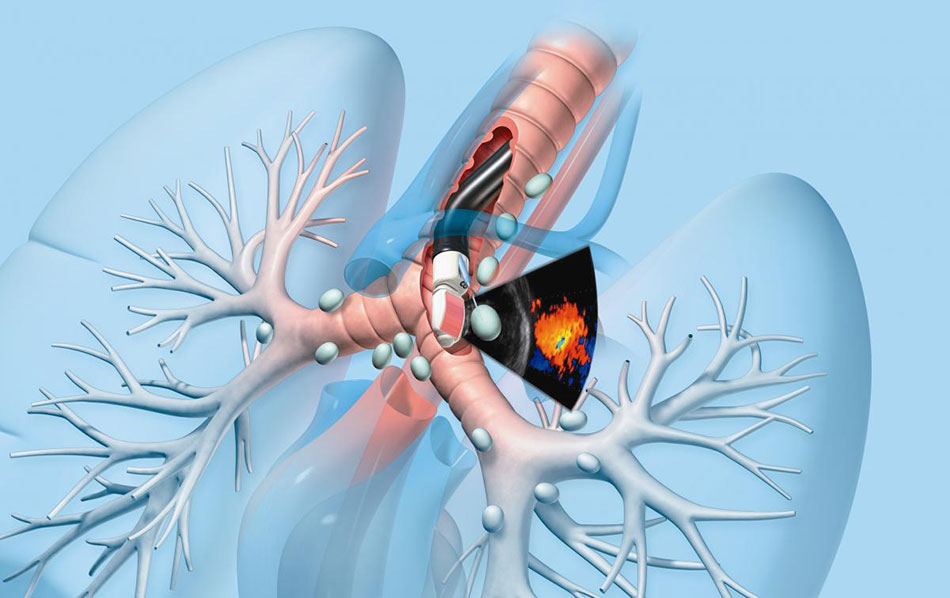
Endobronchial Ultrasound (EBUS) help diagnose lymph nodes in the chest and accurately assess the stage of lung cancer.
Endoscopic ultrasound bronchoscopy with transbronchial lung biopsy (EBUS-TBLB, transbronchial lung biopsy) enables the physician to obtain samples from small opacities or tumours in the distal part of the lung during endoscopic techniques that is not possible with a normal bronchi biopsi. This technique is also used for high-risk patients with transthoracic lung biopsies or in inoperable patients. EBUS-TBLB is done using a small, flexible “endoscope” that is passed through the mouth into the airways that allows the doctor to see inside the lungs and perform the procedure. In this procedure, a radial ultrasound probe is used to help the physician pinpoint the bronchial branch leading to the tumour and ensure that the biopsy forceps reach the tumour in the distal part of the lung. During the endoscopy, very small biopsy forceps are used to obtain a sample of body tissue by piercing the bronchus to reach nearby tumour tissue.
Ultrasonic bronchoscopy with transbronchial needle aspiration (EBUS-TBNA, transbronchial needle aspiration) allows doctors to obtain tissue samples without surgery. In this procedure, a convex ultrasound probe is used to help the physician determine the exact location and size of the mediastinal or hilar lymph nodes and to ensure that the biopsy needle is correctly inserted into the pathologic node to be examined. This method is used to take a sample of ganglion tissue from an area of the body called the mediastinum, which is the part of the ribcage that contains the heart, thymus, oesophagus, trachea, and nerves, inaccessible lymph nodes. In addition, this method also assists in:
- Determining the cause of enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum and/or hilum
- Tuberculosis or sarcoidosis
- Confirmed diagnosis of mediastinal and/or hilar lymph node metastasis from lung and extrapulmonary carcinoma
- Determine the exact stage of lung cancer so that the correct treatment can be administered
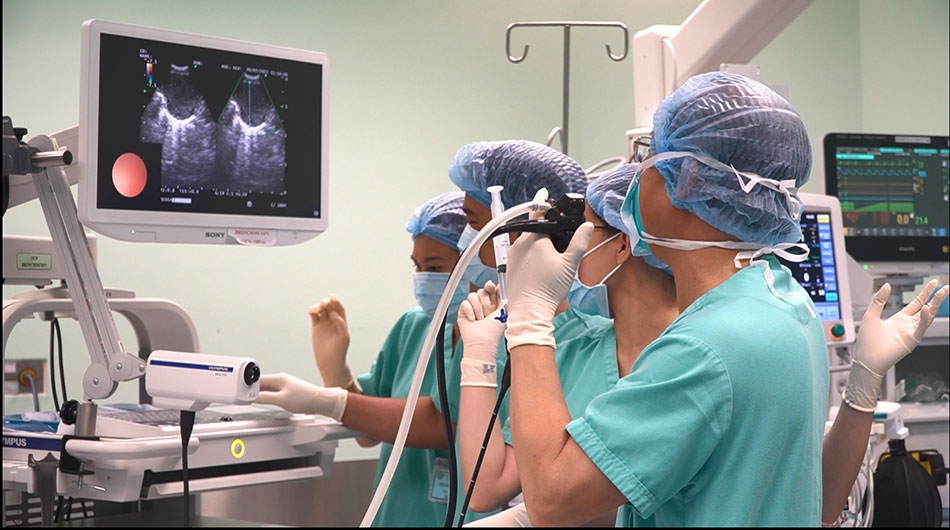
FV Hospital applies and implements EBUS technique at the Internal Medicine Department, Pulmonology Unit by Nguyen Van Tho PhD, MD.
The ultrasound bronchoscopy method is currently a highly appreciated technique to help detect respiratory diseases accurately allowing for timely and effective treatment. the majority of the procedures are uncomplicated and are considered a safe procedure, rarely causing damage to the lungs.
Make an appointment with Nguyen Van Tho, PhD, MD, at the Internal Medicine Department – FV Hospital: (028) 54 11 33 33, ext. 1526

 Vi
Vi 











