WHY GETTING VACCINATED AGAINST COVID-19?
Covid-19 vaccination greatly reduces the chance of you suffering from Covid-19 disease. No vaccine is 100% effective, however studies have shown that, 2 weeks after the second shot, the Moderna Covid-19 vaccine has 94.1% efficacy against symptomatic Covid-19 and an impressive nearly 100% efficacy against severe or critical disease and hospitalisations. This means that the few vaccinated people who do get infected have essentially mild to moderate cases of Covid-19 and that your risk of hospitalisation and death because of Covid-19 is nearly eliminated once you are fully vaccinated.
Also, vaccinated people who might be infected with the coronavirus have fewer virus particles in their nose and mouth and are less likely to spread it to others. This reduced transmission is important as getting vaccinated now not only protects you, but also limits spreading the virus to loved ones, friends and other people.
Reduced transmission is such that, on 13 May 2021, the US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have released an updated guidance saying that fully vaccinated people (2 weeks after their second dose) no longer need to wear a face mask or respect physical distancing in most settings, whether outdoors or indoors.
In addition, recent studies have shown that, after 2 doses, the Moderna Covid-19 vaccine is highly effective at protecting people against specific coronavirus strains (called “variants of concern”) such as the alpha (previously known as Kent), beta (South African), delta (Indian), and gamma (Brazilian) variants.
WHAT IS MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE?
Covid-19 disease is caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus. The Moderna vaccine is a messenger RNA vaccine. It is given to adults aged 18 years and older. The active substance in the vaccine is the mRNA encoding the Covid-19 virus spike protein. This is a protein on the surface of the virus which the virus needs to enter the body’s cells. The mRNA is embedded, to protect it, in oily bubbles made of lipid nanoparticles.
HOW DOES MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE WORK?
After injection, the vaccine particles bump into cells and fuse to them, releasing mRNA. The cell’s “factories” (ribosomes) read its sequence and build spike proteins. The mRNA does NOT interact with the cell’s DNA and is eventually destroyed by the cell, leaving no permanent trace.
The person’s immune system will then recognise this protein as foreign and produce antibodies (by the “B cells”) and activate specific white blood cells (called “T cells”) to attack it.
If, later on, the person comes into contact with SARS-CoV-2 virus, their immune system will recognise it and be ready to defend the body against it.
As Moderna Covid-19 vaccine does not contain the virus to produce immunity, it cannot give you Covid-19.
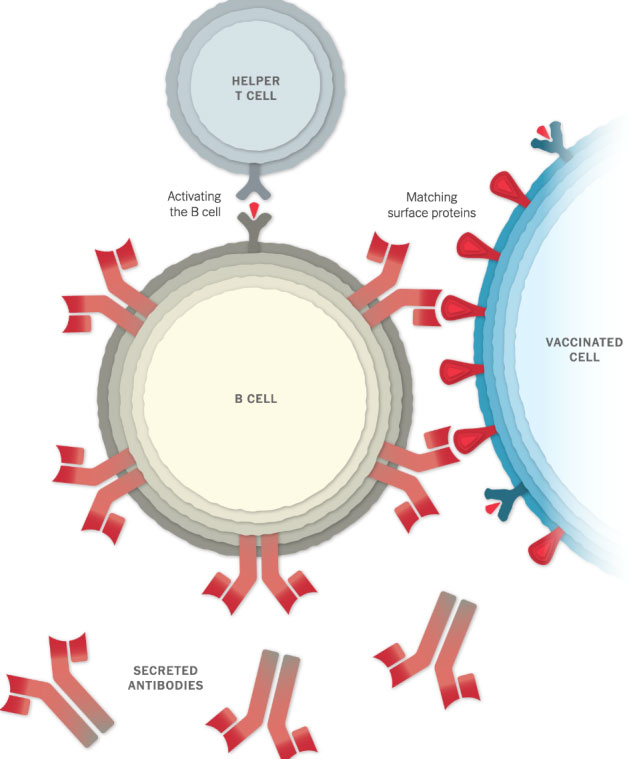
No, the Covid-19 vaccine will not cause a positive test result for a Covid-19 PCR or antigen rapid test. This is because these tests check for active disease and not whether an individual is immune or not. However, because the Covid-19 vaccine prompts an immune response, vaccinated people usually test positive in an antibody (serology) test that measures Covid-19 immunity in an individual.
HOW IS MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE ADMINISTERED?
The Moderna Covid-19 vaccine is injected into a muscle (usually in the upper arm). The vaccine will be given in 2 doses. The second dose must be administered 28 days (4 weeks) after the first dose. You will be advised when exactly to return for your second dose.
Second doses administered within a grace period of 4 days earlier than the recommended date for the second dose are still considered valid. If it is not feasible to adhere to the recommended interval and a delay in vaccination is unavoidable, the second dose of Moderna Covid-19 vaccine may be administered up to 6 weeks (42 days) after the first dose.
Post-vaccination observation times:
- 30 minutes: persons with a history of an immediate allergic reaction of any severity to a vaccine or injectable therapy or a history of anaphylaxis due to any cause;
- 15 minutes: all other persons.
HOW LONG DOES PROTECTION FROM MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE LAST?
Covid-19 vaccination offers good protection within 2 to 3 weeks of the first dose. It takes 2 weeks after getting the second dose to have the best protection, therefore it’s essential to get both doses to protect yourself against Covid-19.
It is not currently known how long the protection given by Moderna Covid-19 vaccine lasts, the immune system contains special cells called memory B cells and memory T cells that might retain information about the coronavirus for years or even decades. Experts therefore believe that immunity from Covid-19 vaccines will last a long time, though it is not known yet whether a booster shot will be required.
CAN CHILDREN BE VACCINATED WITH MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE?
Moderna Covid-19 vaccine is now authorised by the European Medicines Agency for children aged 12 years and older.
CAN IMMUNOCOMPROMISED PEOPLE BE VACCINATED WITH MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE?
Although immunocompromised people (people with weakened immune systems) may not respond as well to the vaccine, there are no particular safety concerns. Immunocompromised people should be vaccinated as they may be at higher risk from Covid-19.
CAN PREGNANT OR BREAST-FEEDING WOMEN BE VACCINATED WITH MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE?
Pregnant women when vaccinated create antibodies to the virus and pass those to their unborn baby through the placenta.
Pregnant people are at increased risk for severe illness from Covid-19. Women with Covid-19 disease are also 2 to 3 times more likely to have their babies early than women without Covid-19 and might be at increased risk of other adverse pregnancy outcomes. Pregnant women with underlying clinical conditions are at even higher risk of suffering serious complications from Covid-19.
For these reasons, it is recommended that pregnant people get vaccinated and are to be treated as priority cases. The vaccine can be given at any stage during pregnancy. There is no reason to delay a pregnancy after Covid-19 vaccination. In addition, Covid-19 vaccines do not affect the fertility of women or men.
Covid-19 vaccines are thought not to be a risk to lactating people or their breastfeeding babies. Actually, mothers were shown to pass antibodies to their newborns through breast milk. Therefore, lactating people can receive a Covid-19 vaccine.

CAN PEOPLE VACCINATED RECENTLY WITH ANOTHER VACCINE RECEIVE MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE?
Covid-19 vaccines and other vaccines may be administered without regard to timing. This includes simultaneous administration of Covid-19 vaccine and other vaccines on the same day, as well as co-administration within 14 days.
CAN PEOPLE WITH PRIOR OR CURRENT COVID-19 INFECTION BE VACCINATED?
People should be offered vaccination regardless of their history of symptomatic or asymptomatic Covid-19 infection.
Vaccination of people with known current Covid-19 infection should be deferred until the person has recovered from the acute illness (if the person had symptoms) and they have met criteria to discontinue isolation.
I HAVE RECEIVED A FIRST DOSE OF ASTRAZENECA COVID-19 VACCINE, CAN I RECEIVE A SECOND DOSE WITH THE MODERNA VACCINE?
For people who have already received a first dose of AstraZeneca, vaccination with a second dose of Moderna is possible and should be done 4 weeks after the first dose but can be given up to 12 weeks after the first dose.
DO YOU HAVE A BLEEDING DISORDER OR ARE YOU TAKING A BLOOD THINNER?
As with all vaccines, Covid-19 vaccine may be given to these patients, if a doctor determines that the patient’s bleeding risk is low enough and the vaccine can be administered intramuscularly with reasonable safety. The following technique for intramuscular vaccination in patients with bleeding disorders or taking blood thinners is recommended: a fine-gauge needle (23-gauge or smaller calibre) should be used for the vaccination, followed by firm pressure on the site, without rubbing, for at least 2 minutes
ARE THERE ANY REASONS YOU SHOULD NOT GET THE VACCINE?
There are very few people who cannot get the Covid-19 vaccine.
The vaccine should not be given to:
- People with known current Covid-19 infection (vaccination should be deferred);
- People who have had a confirmed anaphylactic reaction to any of the ingredients of the vaccine;
- Those who have had a confirmed anaphylactic reaction to a previous dose of the same Covid-19 vaccine.
People with a history of serious allergic reaction to food, an identified drug or vaccine, or an insect sting can get any Covid-19 vaccine, as long as they are not known to be allergic to any component of the Covid-19 vaccine. It’s important that you tell the person giving you your vaccine if you have ever had a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis).
Are you feeling sick today?
There is no evidence that acute illness reduces vaccine efficacy or increases vaccine adverse events. However, as a precaution with moderate or severe acute illness, all vaccines should be delayed until the illness has improved. Mild illnesses (e.g., upper respiratory infections, diarrhoea) are NOT contraindications to vaccination. Do not withhold vaccination if a person is taking antibiotics.
WHAT ARE THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH MODERNA COVID-19 VACCINE?
Like all medicines, vaccines can cause side effects. So far, millions of people have been given the Moderna Covid-19 vaccine and reports of serious side effects have been very rare. No long-term complications have been reported. Most of the Moderna Covid-19 vaccine side effects are mild and short-term (a few days), and not everyone gets them (about 10-20% of people), they include:
- A sore arm where the needle went in, with sometimes redness and swelling
- Feeling tired
- A headache
- Feeling achy
- Nausea
- Swelling of the face
- Some people will experience mild flu-like symptoms
- Very few people get a high temperature or feel hot or shivery 1 or 2 days after vaccination
- An uncommon side effect is swollen glands in the armpit or neck on the same side as the arm where you had the vaccine. This can last for around 10 days, but if it lasts longer see your doctor.
Very rare cases of inflammation of the heart (myocarditis or pericarditis) have been reported following vaccination with Moderna Covid-19 Vaccine. These have happened most often in younger men and shortly after the second dose of the vaccine. Most of these cases were mild and people recovered soon after with simple treatment and rest.
Allergic reactions (hypersensitivity) have been seen in people receiving the vaccine. Cases of anaphylaxis (severe allergic reaction) are very rare. If you do have a reaction to the vaccine, it usually happens in minutes. Signs of an allergic reaction may include itchy skin rash, shortness of breath and swelling of the face or tongue.
As for all vaccines, Moderna Covid-19 vaccine should be given under medical supervision, with the appropriate medical treatment available in case of allergic reactions. Staff giving the vaccine are trained to deal with allergic reactions and treat them immediately.
ARE THE SIDE EFFECTS DIFFERENT FOR EACH DOSE?
Side effects can occur after the first and/or the second dose. Even if you did have side effects after the first dose, you still need to have the second dose (except if you had a severe allergic reaction after the first dose).
WHAT SHOULD YOU DO IF YOU ARE EXPERIENCING SIDE EFFECTS?
If you are experiencing side effects, rest until you feel better. You can take pain killers, such as paracetamol, if you need to.
You should seek medical advice:
- If your symptoms seem to get worse or if you are concerned;
- If you have swollen glands for more than 10 days;
- In case of abnormal, persistent symptoms, such as high fever for more than 4 days.
- It is important that you urgently seek medical attention if you experience new onset of symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath or feelings of having a fast-beating, fluttering, or pounding heart.
You can contact, at any time, FV Hospital Accident & Emergency Department at
References
- Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine – New England Journal of Medicine 4 Feb 2021
- Prevention and Attenuation of Covid-19 with the mRNA Vaccines – New England Journal of Medicine 30 June 2021
- Clinical information for vaccine consenters: Moderna vaccine.
- London Covid-19 Vaccine Pharmacy Group (NHS). https://www.ncl-mon.nhs.uk/wp-content/uploads/Guidelines/0_Moderna_Information_for_vaccinators.pdf
- Everything you need to know about Covid-19 vaccines. The Pharmaceutical Journal, May 2021; Online: DOI:10.1211/PJ.2021.1.71237
- Clinical Considerations for Use of Covid-19 Vaccines. Centers for Disease Control. https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/covid-19/clinical-considerations/covid-19-vaccines-us.html
- Coronavirus (Covid-19) vaccine. NHS. https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/coronavirus-covid-19/coronavirus-vaccination/coronavirus-vaccine/
- Important information about pregnancy and breastfeeding. NHS Scotland. nhsinform.scot/covid19vaccinepregnancy
- Covid-19 vaccines and pregnancy. Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists. https://www.rcog.org.uk/covid-vaccine
- Covid-19 Vaccines While Pregnant or Breastfeeding. Centers for Disease Control. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/vaccines/recommendations/pregnancy.html
- Using Covid-19 vaccines in women of child bearing potential.
- Public Health England’s Immunisation Against Infectious Disease (The Green Book).
Download:

 Vi
Vi