In order to improve the breadth of services offered at the Cardiology Department, FV is launching a well-equipped catheterisation laboratory, helping patients with cardiac problems to benefit from having cardiac intervention procedures, both simple and complicated, performed here at the hospital.
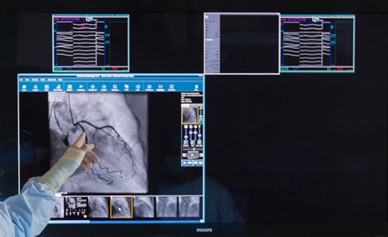
FV Hospital’s new 60-square-metre Catheterisation Laboratory is located in the OT and is fully equipped with advanced equipment to enable physicians to diagnose cardiac conditions and perform intervention procedures.
FV’s physicians are available 24 hours a day to offer timely medical assistance in case of a heart attack.
The diagnosis and intervention procedures performed at Catheterisation Laboratory include:
Coronary artery scan
A catheter is inserted through the skin into an artery (usually in the upper thigh or wrist) and then is threaded through the body’s arterial highway to the heart, where a special dye is injected into the coronary arteries to reveal any possible blockages.
Balloon angioplasty
During this procedure, a catheter with a balloon on its tip is passed through to a coronary blockage. The balloon is inflated, splitting the plaque and stretching the wall of the coronary vessel to allow more blood to flow to the heart muscle.
Stenting
A stent is a small, metal mesh tube that is placed within a coronary artery after balloon angioplasty to prevent the artery from reclosing. In some cases, doctors may recommend drug-eluting stents coated with a special medication to further help prevent re-narrowing of the coronary arteries. Like other coronary stents, it is left permanently in the artery, and slowly releases a drug that prevents the build-up of tissue that leads to restenosis.
Septal defect closure
Septal defects (atrial septal defect [ASD] and ventricular septal defect [VSD]) and large arteries (patent ductus arteriosus) will affect arterial blood pressure and heart function. A wire mesh device made out of nickel and titanium and filled with a polyester thread is used to close defects and stabilise arterial blood pressure and heart function.
Pulse generator implantation
An irregular heartbeat, too fast or too slow, can seriously affect the blood-pumping function of the heart and cause fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, fainting and even death. Cardiologists will recommend cardiac pacemaker implantations if medical treatment is not effective.
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD), a pacemaker and cardiac resynchronisation therapy (CRT) are three devices that can be implanted at FVH Catheterisation Laboratory.
These procedures for arrhythmia treatment are usual performed under local anaesthesia. The devices will be inserted through a small incision on the left side of the chest. The insulated wire is inserted into an axillary vein or a major vein under your collarbone and is secured to the appropriate position in your heart, while the other end is attached to the pulse generator, which is programmed to control your heart rate. This is a safe and effective procedure which has almost no risk of complication.

 Vi
Vi 












